- Solutions
- Insights
- Company
- Get in Touch
Smart Platforms and Analytics for a Digital Future
Transform decision-making at scale with our Gen AI predictive analytics platforms

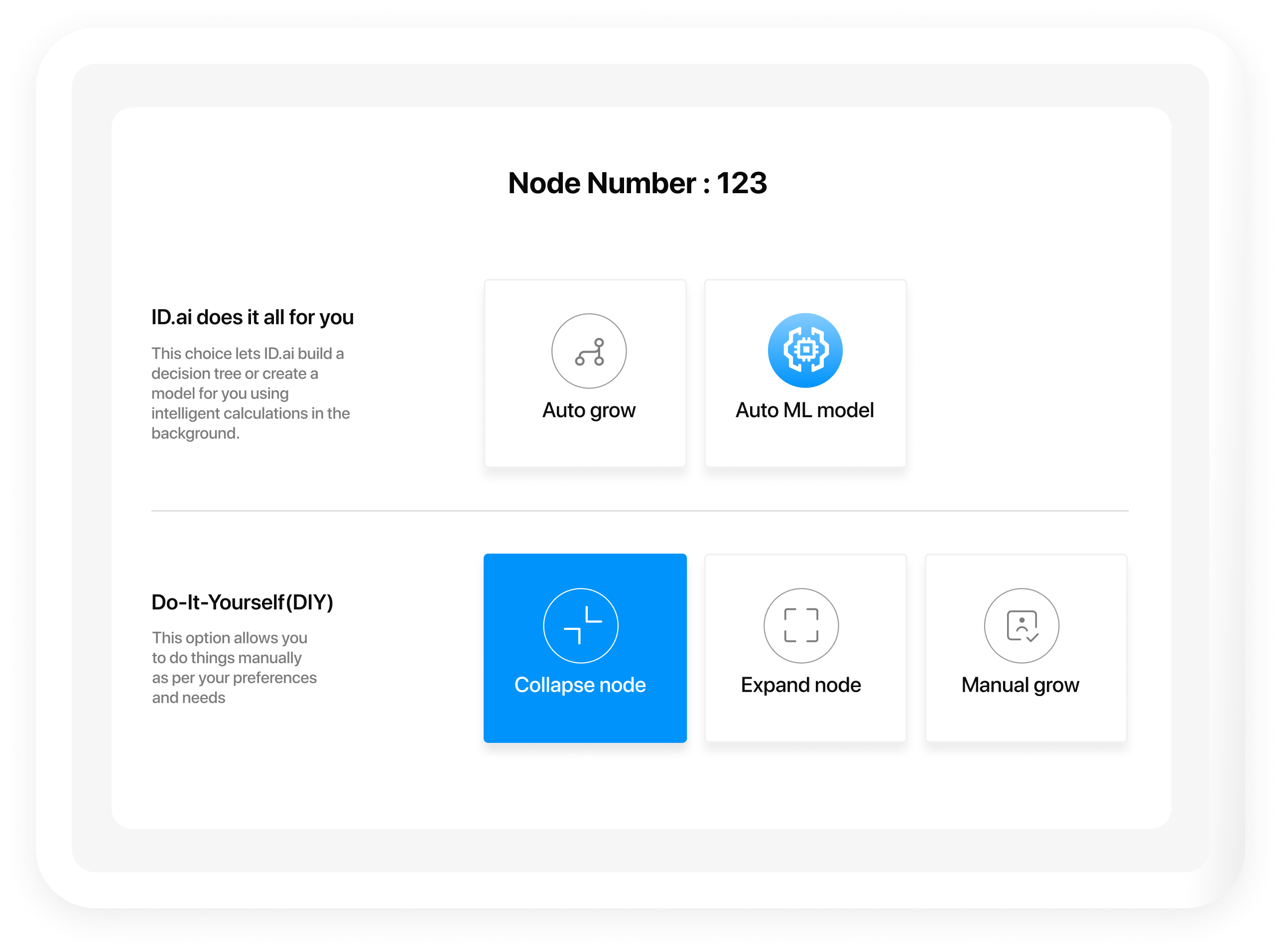
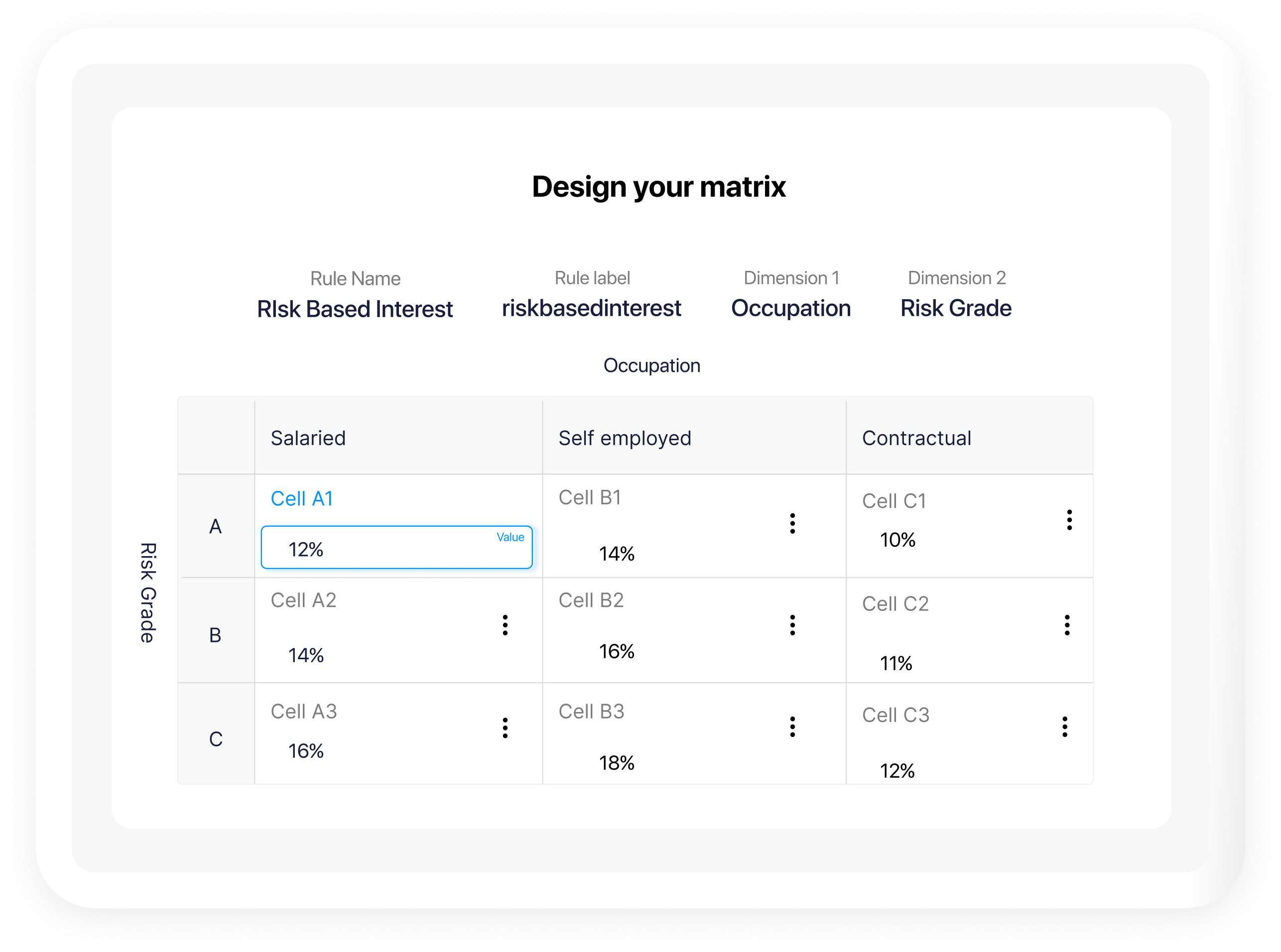
Corestrat's offerings
Corestrat’scase studies
Our solutions enable top institutions across sectors to enhance risk management, automate decisions, streamline loan origination, and extract valuable insights from vast datasets.
Learn more about how these industry leaders are leveraging our solutions to excel in their operations and achieve enhanced ROI.

Why choose Corestrat?
Scalable & secure
Our solutions are built on cloud-native architecture, ensuring scalability, security, & easy integration with your existing systems
Proven expertise
With years of expertise in AI-powered risk management & decision automation, we’ve become a trusted partner for leading organisations
Tailored solutions
Every institution has unique challenges & goals, so our AI-powered solutions are flexible, customisable, & built to adapt to your needs
Innovative approach
We prioritise innovation, rigorous analytics and due diligence to deliver intelligent, future-ready solutions

Our numbers speak
for themselves
Efficiency
Improvement through smart workflow automation
Accuracy
Improvement in predictive models
Return on investment
On scalable portfolio management platforms
Cost Savings
For organisations through automated decision making
What our customers say
Hear directly from our core clients about how our decision management software has helped them innovate, streamline operations, and achieve their business goals.

"Centralised rule management"
We've been using Corestrat's DLA and Rule.ai for months, and it has greatly streamlined our policy management and decision-making. The no-code interface makes policy creation effortless, seamlessly integrating internal and external data. The centralised rule management hub ensures efficient tracking and updates, empowering our product and risk teams. Plus, integrating with IntelliDecision.ai enables rapid predictive modelling and cut-off setting, giving us a competitive edge.
Vishu Ramchandran
Chairman & Managing director
Gosree Finance Limited

"Smarter decisions, driven by data."
Corestrat’s Decision Intelligence Capability has given us at ACI Logistix the visibility and direction we needed to drive efficiency and reduce costs. With Corestrat's intelligent decisioning platforms, we can truly understand parcel-level profitability, track operating expenses, and monitor SLA performance, turning our data into a powerful decision-making engine. It has enabled us to identify inefficiencies, protect margins, and confidently refine our pricing and service strategies. By providing a complete 360° view of our parcel economics, Corestrat ensures our decisions are firmly based on data. This has strengthened our position in the logistics market and, most importantly, helped us earn greater customer satisfaction and trust in our brand.
Keith Somers
CEO
FAST Group
Let's get Started!
Our experts are happy to connect with you to explore how we can help your enterprise innovate
Hear from our experts
One-on-one demo of our solutions
Next-gen technology & features